Which Pedigree Symbol Is Used To Represent A Female Carrier Of A Recessive X-linked Trait?
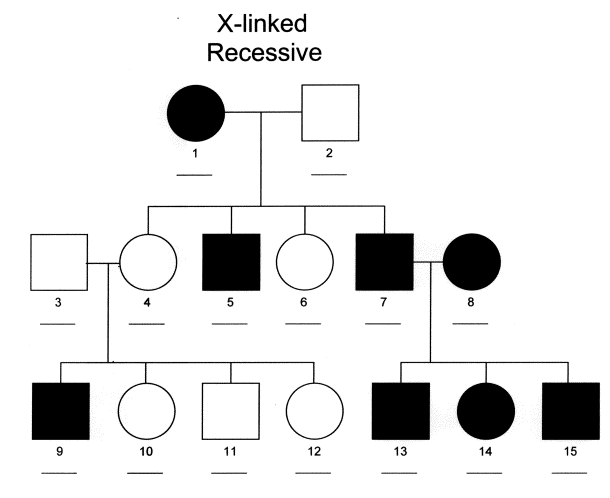
Sex (Ten)-linked Recessive Inheritance Blank Pedigree (PDF)
Sex (X)-linked Recessive Inheritance Full-blooded Example Answers (PDF)
When completing this pedigree with Ten-linked recessive inheritance, apply the symbols 10 and Y in the genotype to represent the sex chromosomes passed on from the previous generation. The X chromosome will comprise the alleles for the trait and the Y chromosome will accept no alleles for this trait. When completing this pedigree with X-linked recessive inheritance, shaded females who are expressing the recessive phenotype and can only have the genotype of XrXr, the shaded males who are expressing the recessive phenotype and can but have the genotype of XrY, and the non-shaded males who are expressing the dominant phenotype and can only accept the genotype XRY. Use this cognition and boosted noesis about how genes are passed from generation to generation to complete the rest of the full-blooded.
Patterns for X-linked Recessive Inheritance
After filling in the genotypes for individuals in several family trees that exhibit this mode of inheritance, some patterns that tin can be noticed are:
- The trait is more common in males than in females.
- If a mother has the trait, all of her sons should also accept it.
- There is no male to male transmission.
- It has the same inheritance patterns as autosomal recessive for human females.
- The son of a female person carrier has a 50 percent take chances of having the trait.
- Mothers of males who have the trait are either heterozygous carriers or homozygous and limited the trait.
Real Examples: Hemophilia, Muscular Dystrophy and Fragile X.
Recall:
- The father passes his X sex activity chromosome (and all its genes) to his daughters and his Y sex chromosome (with its genes) to his sons.
- Genes human activity in pairs, one from each parent for the females. For this mode of inheritance, males get their gene for the trait from their mother.
- Gene pairs carve up during meiosis and the formation of the sex activity cells along with the chromosomes.
- When the sperm fertilizes the egg, the father's genes (and chromosomes) bring together the female parent's, or both contribute to the genetic makeup of the offspring.
- One form of a cistron may exist dominant over another form which is recessive and the dominant grade would be expressed.
X-inactivation
X-inactivation, also known as lyonization afterwards Mary Lyon who discovered the phenomenon, is a process by which ane of the copies of the 10 chromosome nowadays in female mammals is inactivated very early in embryonic evolution. In Twenty females, the bulk of the genes on the X chromosome are silenced. This stops females from having twice equally much gene production compared to males. The choice of which Ten chromosome is inactivated is random and should occur at approximately a 50/50 ratio. If this inactivation does not occur at a 50/50 ratio information technology is called skewed Ten-inactivation, or skewed lyonization. Skewed X-inactivation causes more gene product from one X to be expressed, which can disrupt the typical "X-linked recessive" model. If more than of the factor product from the variant (mutated) gene is expressed in a female, the "10-linked recessive" condition may exist expressed. A female person tin can have symptoms ranging from astringent (like a male) to a milder signs and symptoms. A woman with skewed X-inactivation will still pass down the cistron variant to half of her children, with males being affected and females typically being unaffected 'carriers'. It is of import to think that some conditions, such as hemophilia, may non always follow the typical "X-linked recessive" model and may have heterozygous females that show signs and symptoms.
Other things to go along in mind:
- A female with Turner syndrome will only take one X and will therefore limited "X-linked recessive" conditions just equally a male would
- A female with an 'XXX' genotype may accept a unlike Ten-inactivation pattern
- A male with an 'XXY' genotype may express milder phenotype due to his X-inactivation pattern
Which Pedigree Symbol Is Used To Represent A Female Carrier Of A Recessive X-linked Trait?,
Source: https://migrc.org/teaching-tools/genetic-inheritance-patterns/sexx-linked-recessive/
Posted by: bowennack1994.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Pedigree Symbol Is Used To Represent A Female Carrier Of A Recessive X-linked Trait?"
Post a Comment